What Is The Template Strand Of Dna
What Is The Template Strand Of Dna - The coding strand of the dna has the same sequence as that of the mrna; This template strand is called the noncoding strand. It is always opposite or complementary to the template strand. Adenine (a), thymine (t), guanine (g) and cytosine (c). Web shown below is a long template strand (= parent strand) of dna where lagging strand dna synthesis is occurring. Even if there are only a few cells present in. It runs in the five prime (5’) to three prime (3’) direction. The dna strand that would correspond to the mrna is called the coding or sense strand. Web anatomy & physiology 2. In a cell, antisense dna serves as the template for producing messenger rna (mrna), which directs the synthesis of a protein.
DNA Strands PowerPoint Template SlideModel
The other strand, the coding strand, is identical to the rna transcript in sequence, except that it has uracil (u) bases in place of thymine (t) bases. During transcription, the template strand, also known as the ‘minus’ or ‘antisense’ strand, is generated by rna polymerase itself in the case of. The template strand runs in a 3′ to 5′ direction..
Dna Template Strand shatterlion.info
During dna replication, the template is generated by enzymes known as helicases. During transcription, the template strand, also known as the ‘minus’ or ‘antisense’ strand, is generated by rna polymerase itself in the case of. Web a template strand is the term that refers to the strand used by dna polymerase or rna polymerase to attach complementary bases during dna.
35 Can You Label The Way Nucleotides Pair Up In Replicating Dna
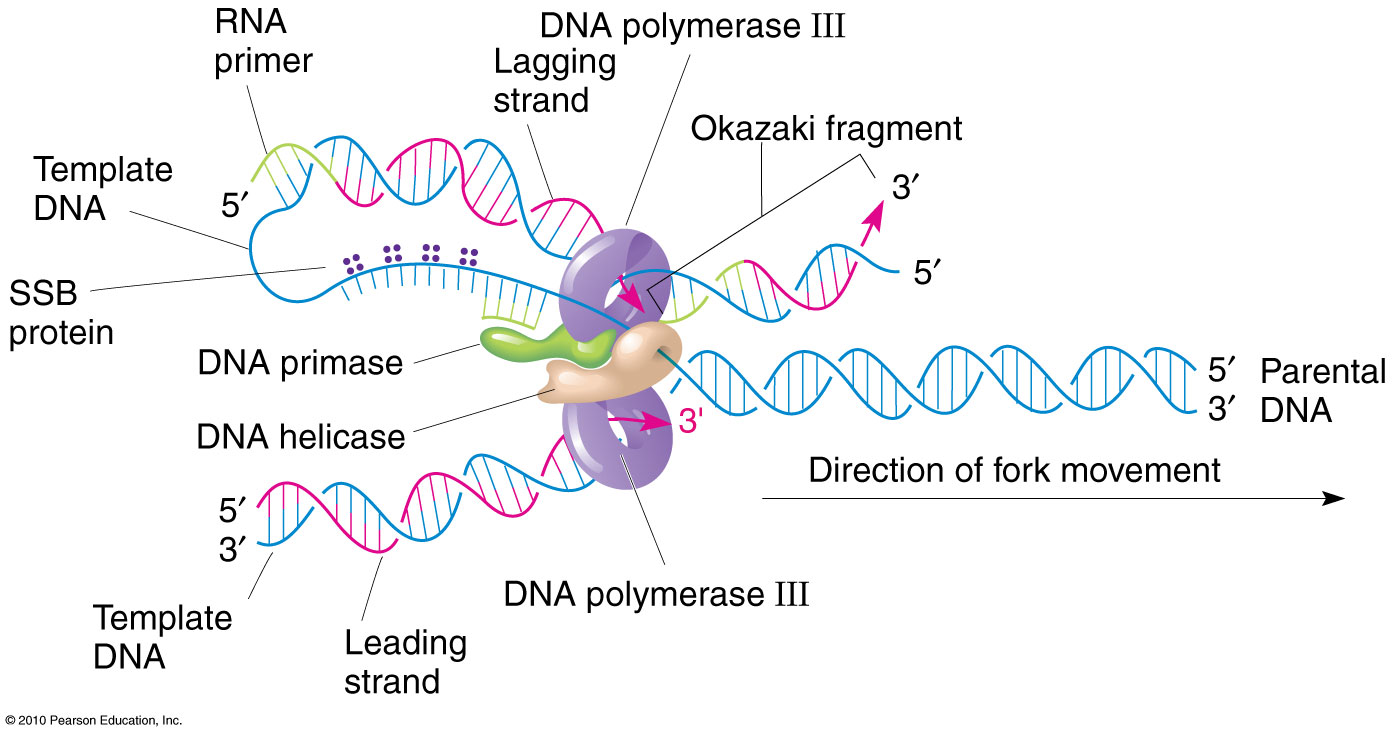
These enzymes utilize energy from atp to move on dna, destabilize the hydrogen bonds between bases, and separate the two strands of the double helix. During dna replication, the template is generated by enzymes known as helicases. The template strand is the one that rna polymerase uses as the basis to build the rna. The four types of nitrogen bases.
DNA Replication Study Solutions
When referring to dna transcription, the coding strand (or informational strand) is the dna strand whose base sequence is identical to the base sequence of the rna transcript produced (although with thymine replaced by uracil). It runs in the five prime (5’) to three prime (3’) direction. The order, or sequence, of these bases determines what biological instructions are contained.
Answered Template strand New strand New strand… bartleby
The other strand, the coding strand, is identical to the rna transcript in sequence, except that it has uracil (u) bases in place of thymine (t) bases. (your answer must be written 5'→3'.) how would the sequence be different if rna were made from this dna template? Web a template strand is the term that refers to the strand used.
Dna Templating
[1] this technique offers a wide variety of applications, including the identification of sister chromatid exchanges in the parental cell prior to. Web shown below is a long template strand (= parent strand) of dna where lagging strand dna synthesis is occurring. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. Web the other strand of dna, besides the template.
Coding Strand of DNA bartleby
The coding strand is the dna strand whose base sequence is similar to its. The office template features several alternatives of the helix. Web the dna strand that mrna is built from is called the template strand because it serves as a template for transcription. Web the template strand of dna is the strand that is used during transcription to.
The coding strand of DNA is 5'AATTCAAATTAGG3'
Impress your audience with the dna strands powerpoint template. It is also called the antisense strand. Web anatomy & physiology 2. It runs in the five prime (5’) to three prime (3’) direction. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up.
The Diagram Below Shows A Double Stranded Dna Molecule Parental Dna
Web the template strand of dna is the strand that is used during transcription to produce rna. The order, or sequence, of these bases determines what biological instructions are contained in a. The coding strand is the dna strand whose base sequence is similar to its. Web this dna is used as a template for polymerase chain reaction,. New dna.
Chapter The Code — The Biology Primer
The template strand runs in a 3′ to 5′ direction. In a cell, antisense dna serves as the template for producing messenger rna (mrna), which directs the synthesis of a protein. The dna strand that would correspond to the mrna is called the coding or sense strand. During dna replication, one new strand (the leading strand) is made as a.
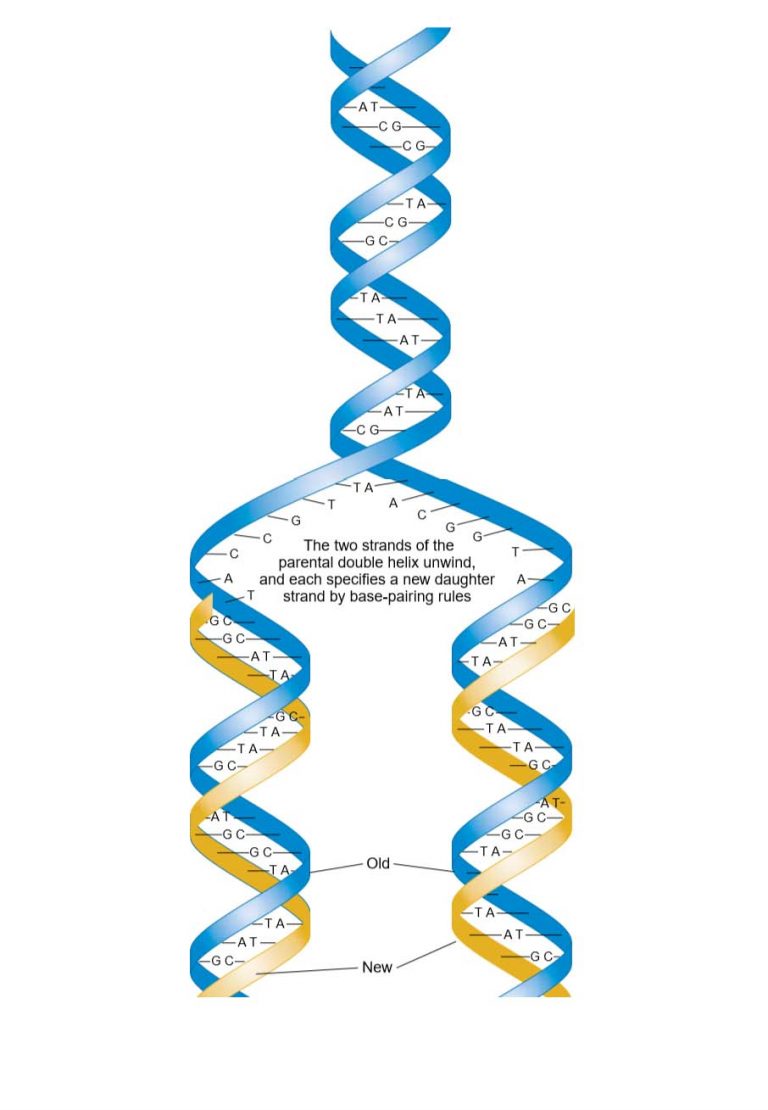
Web in molecular biology and genetics, the sense of a nucleic acid molecule, particularly of a strand of dna or rna, refers to the nature of the roles of the strand and its complement in specifying a sequence of amino acids. Web each strand in the double helix acts as a template for synthesis of a new, complementary strand. Web shown below is a long template strand (= parent strand) of dna where lagging strand dna synthesis is occurring. The order, or sequence, of these bases determines what biological instructions are contained in a. Web the other strand of dna, besides the template strand, is known as the coding strand. It is also called the antisense strand. The dna strand that would correspond to the mrna is called the coding or sense strand. Web 1 day agothis dna is used as a template for polymerase chain reaction, or pcr, analysis, a method that is essentially the xerox copier of molecular biology. In a cell, antisense dna serves as the template for producing messenger rna (mrna), which directs the synthesis of a protein. Web the dna strand that mrna is built from is called the template strand because it serves as a template for transcription. The template strand runs in a 3′ to 5′ direction. Web a template strand is the term that refers to the strand used by dna polymerase or rna polymerase to attach complementary bases during dna replication or rna transcription, respectively; Either molecule moves down the strand in the 3′ to 5′ direction, and at each subsequent base, it adds the complement of the current. Adenine (a), thymine (t), guanine (g) and cytosine (c). These enzymes utilize energy from atp to move on dna, destabilize the hydrogen bonds between bases, and separate the two strands of the double helix. Even if there are only a few cells present in. Web the template strand of dna is the strand that is used during transcription to produce rna. Cell chemistry & cell components nucleic acids. Impress your audience with the dna strands powerpoint template. Web anatomy & physiology 2.